Abstract
INTRODUCTION: For decades, ABVD (doxorubicin, bleomycin, vinblastine, dacarbazine) has been the standard of care for frontline (1L) treatment of classic Hodgkin lymphoma (cHL); however, ~30% of advanced stage (III/IV) patients are refractory to or relapse following ABVD. PET-adapted strategies, consisting of treatment escalation or de-escalation based on interim PET scan results after 2 ABVD cycles (Johnson 2016), and novel targeted agents have emerged to minimize toxicity and reduce bleomycin exposure. The ECHELON-1 6-year follow-up data demonstrated a 41% reduction in the risk of death with A+AVD (brentuximab vedotin, doxorubicin, vinblastine, dacarbazine) vs ABVD (HR: 0.59; 95% CI: 0.40-0.88; P=0.009) in newly diagnosed stage III/IV cHL patients (Ansell 2022), the first regimen to show improvement in overall survival (OS) vs ABVD in this setting. As patients enrolled in clinical trials may differ from those treated in real-world settings, this study assessed real-world characteristics, treatment patterns, interim PET scan use, and clinical outcomes for US patients with stage III/IV cHL treated with 1L ABVD.
METHODS: This is a retrospective observational study of structured/unstructured data from the de-identified electronic health record (EHR)-derived Flatiron Health research database (FHRD; 1/1/2011-8/31/2020). Patients included had cHL identified by ICD-9/ICD-10 codes, ≥2 documented visits as identified by structured data, pathology consistent with a cHL diagnosis as confirmed in unstructured data, age ≥18 years at diagnosis, and evidence of medication administration or non-canceled order for an antineoplastic, as identified by structured data. Nodular lymphocyte-predominant HL patients were excluded. Those who met inclusion criteria entered a broad cohort; this analysis includes data from a random sample of stage III/IV cHL patients treated with 1L ABVD. Data analyzed included baseline disease and clinical characteristics, GCSF and PET scan use, treatment modification, subsequent therapy, and survival. Results are summarized descriptively and survival rate was estimated using the Kaplan Meier method.
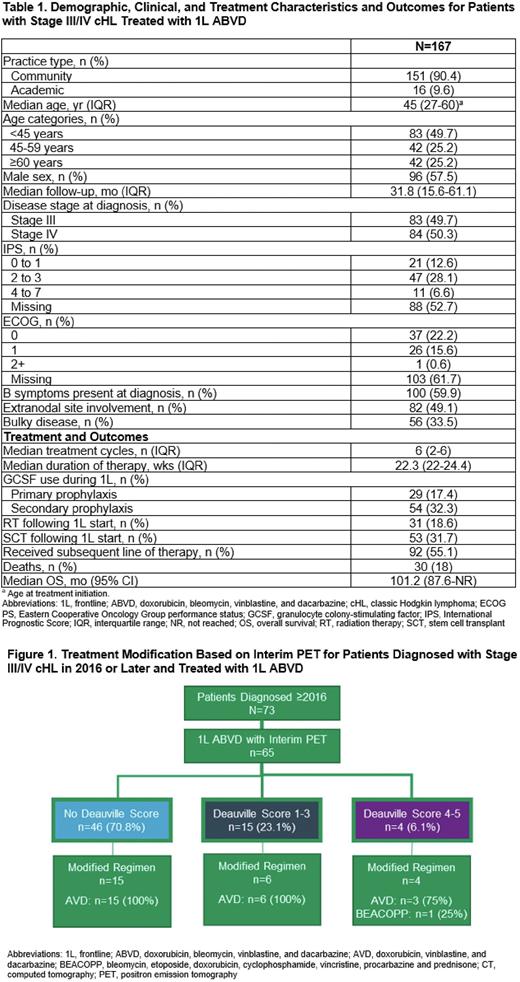
RESULTS: Data were analyzed for 167 stage III/IV cHL patients treated with 1L ABVD. Median (IQR) age at treatment initiation was 45 (27-60) years (Table 1). EHR-derived IPS scores of 0-3 and 4-7 were documented for 41% and 7% of patients; ECOG PS of 0-1 and ≥2 were documented for 38% and <1% of patients. Among all patients, 49% had extranodal disease, 60% had B symptoms, and 34% had bulky disease. Patients received a median (IQR) of 6 (2-6) ABVD doses, with a median (IQR) duration of therapy of 22.3 (22-24) weeks. GCSF was given to 50% of patients treated with 1L ABVD (primary prophylaxis: 17%; secondary prophylaxis: 32%), with a mean (SD) of 5.5 (7.7) doses given. A baseline PET scan was obtained for 61% and an interim PET scan for 90% of patients during treatment with 1L ABVD after a median (IQR) of 72 (53-109) days. Of patients diagnosed in 2016 or later (44%, n=73), 64% received a baseline PET scan and 89% received an interim PET scan after a median (IQR) of 55 (50-68) days; Deauville scores were documented for 29% (score 1-3, 23%; score 4-5, 6%) and SUV scores were documented for 63%. Of patients who received an interim PET scan (n=65), those that de-escalated therapy included 15/46 with no documented Deauville score, 6/15 with a score of 1-3, and 3/4 with a score of 4-5 (Figure 1). Among all patients, 19% received radiation therapy (RT), 55% received subsequent therapy, and 32% received a stem cell transplant (SCT; autologous: n=48, allogeneic: n=4) following 1L ABVD treatment. Median (IQR) time from start of 1L ABVD to RT, subsequent therapy, or SCT was 9.5 (6.6-24.1), 10.6 (6.9-17.3), and 15.9 (11.7-24.0) months, respectively. At a median (IQR) follow-up of 31.8 (15.6-61.1) months, 82% of patients were alive, with a median OS (95% CI) of 101.2 (87.9-not reached) months; estimated 2-year OS (95% CI) was 94.4% (89.1%-97.2%).
CONCLUSION: This FHRD analysis shows that stage III/IV cHL patients treated with 1L ABVD in the real world were older and had higher rates of RT, subsequent therapy, and SCT than seen in clinical trials. GCSF was given to 50% of patients, for most as secondary prophylaxis. For patients diagnosed in 2016 or later, interim PET scans and Deauville scores were not universally obtained after cycle 2. Despite this, de-escalation to AVD was observed; only 1 patient was escalated to BEACOPP.
Disclosures
Winter:Janssen: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Seagen, Inc: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; OncLive: Honoraria. Liu:Seagen, Inc: Current Employment, Current equity holder in publicly-traded company. Surinach:Seagen, Inc: Consultancy. Fanale:Seagen, Inc: Current Employment, Current equity holder in publicly-traded company. Yu:Seagen, Inc: Current Employment, Current equity holder in publicly-traded company. Narkhede:Roche: Research Funding; Gilead: Research Funding; Genetech: Research Funding; Genmab: Research Funding; Gilead/Forty-seven: Research Funding; EUSA pharmaceuticals;: Research Funding; ADC Therapeutics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; TG Therapeutics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Seagen Inc.: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal